List Three Ways Coenzymes Work
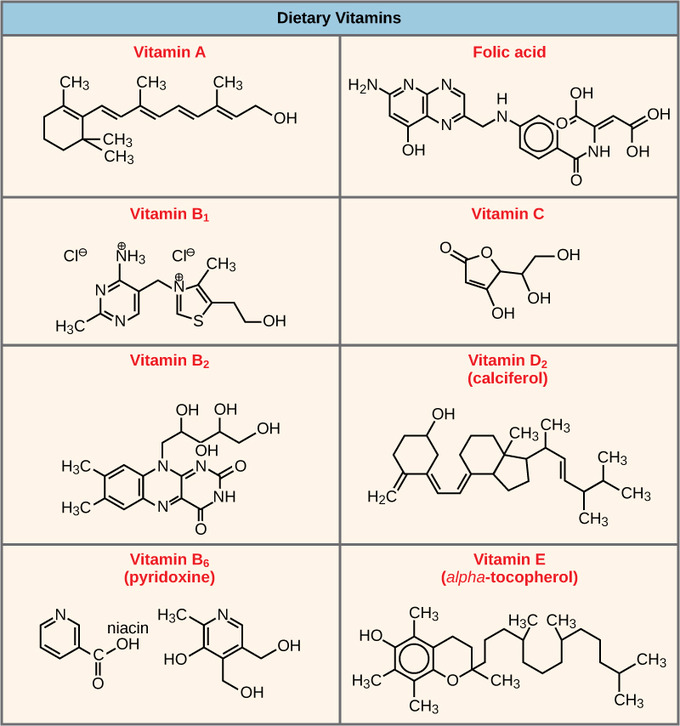
The coenzyme is involved in transfer of acyl-groups. Vitamin B-2 or riboflavin is the precursor for the flavin coenzymes flavin mononucleotide or FMN and flavin adenine dinucleotide or FAD.

5 Tips To Anti Aging Naturally The Anti Aging Guide Skincare Antiaging Best Anti Aging Creams Anti Aging Skin Products Anti Aging Skin Care
As the prefix co- suggests they work with enzymes.

List three ways coenzymes work. Many coenzymes are derived from vitamins. A cofactor may be a metalsuch as iron copper or magnesiuma moderately sized. The sulfhydryl -SH group of cysteamine moiety of this coenzyme forms a thioester with the carboxyl -COOH group of the acyl-compound.
Coenzymes work by binding to the active side of the enzymes the side that works in the reaction. They affect every function from breathing to digestion. Coenzyme plays a role in the functioning of cells.
Give the structure and biochemical function of any 3 coenzymes. Coenzymes are small organic molecules that link to enzymes and whose presence is essential to the activity of those enzymes. The other type of cofactors called prosthetic groups work in much the same way as coenzymes.
Coenzyme A CoA SHCoA CoASH is a coenzyme notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. It can be considered a helper molecule for a biochemical reaction. Reactions within the cells work to break down the nutrients.
1 mono-ADP-ribosylation 2 poly-ADP-ribosylation 3 NAD-dependent deacetylations 4 formation of cyclic ADP-ribose. There are several ways coenzymes assist in enzyme function including changing their shape to activate or turn on enzymes or aiding in chemical reactions by acting as carriers of energy or. It is achieved in three ways.
1 Define coenzyme. Some coenzymes function by ferrying electrons or negative charges to enhance a reaction. Coenzymes hold an atom or group of atoms allowing an enzyme to work.
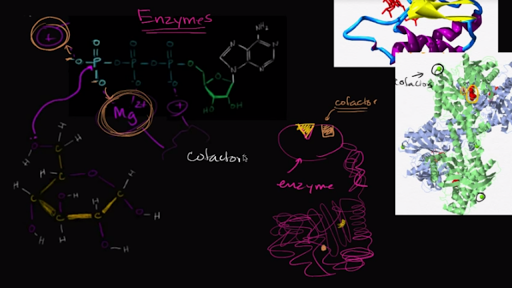
Ie they have a protein component and a so-called cofactor. PLP Biotin Hemes Cobalamin TPP Lipoamide FAD building blocks of coenzymes. If the cofactor is removed the protein no longer enzymatically active is called the apoenzyme.
Coenzymes belong to the larger group called cofactors which also includes metal ions. Vitamin K 2 of bacterial origin and Vitamin K 3 of synthetic origin. Since enzymes and coenzymes are nonmetal organic molecules they bind together by.
Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the body. Bavik in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition Second Edition 2003 Vitamins. Coenzymes are nonprotein organic molecules that facilitate the catalysis or reaction of its enzyme.
And combine molecules for cellular activities that keep the cells alive. These small organic cofactors can then take part in further enzymatic reactions. Examples of coenzymes include the B vitamins and S-adenosyl methionine.
A coenzyme is an organic non-protein compound that binds with an enzyme to catalyze a reaction. A coenzyme is a substance that works with an enzyme to initiate or aid the function of the enzyme. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate and around 4 of cellular enzymes use it or a thioester as a substrate.
Coenzymes are often broadly called cofactors but they are chemically different. Protein - protein - Cofactors. A substance that enhances the action of an enzyme.
Enzymes are the. Although some enzymes consist only of protein many are complex proteins. A complete enzyme is called a holoenzyme.
Lipases for example help digest fat. Vitamins B-2 B-3 and C are all precursors of electron-carrying coenzymes. 2 Write a short note on Thiamine.
Structure and Biochemical function. Enzymes accelerate these reactions. Vitamin K 1 abundant in any diet and of vegetable origin.
Cofactor is the more general term for small molecules required for the activity of their associated enzymes. Like steps in a relay triathlon except with way more than three events. All of the water-soluble vitamins and two of the fat-soluble vitamins A and K function as cofactors or coenzymesCoenzymes participate in numerous biochemical reactions involving energy release or catabolism as well as the accompanying anabolic reactions Figure 1.
There are different variants of ADP-ribosylation. Type of coenzyme that remains bound to active site of the enzyme and requires a second chemical reaction at that site to return to its coenzyme state tightly bound to enzyme Examples. The temporary binding between coenzymes and their apoenzymes means coenzymes can easily detach themselves from the enzyme after a biochemical reaction occurs.
A coenzyme cannot function alone but can be reused several times when paired with an. 3 Write a short note on any 5 coenzyme. Coenzyme A has a complex structure consisting of an adenosine triphosphate a pantothenic acid which is a B-vitamin and cysteamine.

Coenzyme An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Coenzyme An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Coenzymes Cofactors Metabolism Assays Biovision Inc

Coenzyme Definition Function Examples Biology Dictionary

Science Of Skincare Makeup On Instagram Hi Friends Here Are Some Quick Beauty Lab Notes I Will Make A Separate Detailed Post On Each Of T Hudvard

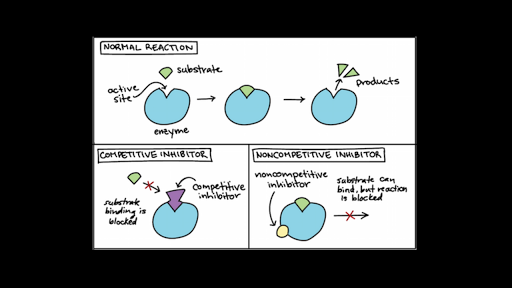
Enzyme Cofactors And Coenzymes Video Khan Academy
Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy

Energy Matter And Enzymes Microbiology

Nucleotide Coenzymes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Enzyme Cofactors And Coenzymes Video Khan Academy

Coenzymes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics





Posting Komentar untuk "List Three Ways Coenzymes Work"