Facilitated Diffusion Moves Large Molecules Through What
Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion is the flow of chemicals and other substances to a region of low concentration from a region of high concentration. Facilitated diffusion is a spontaneous process in which charged ions or molecules are transported across the lipid-based cell membrane via a carrier transmembrane protein molecule.

Pin On Chapter 25 The Digestive System
In other cases the protein changes shape allowing molecules to pass through.

Facilitated diffusion moves large molecules through what. FACILITATED DIFFUSION In facilitated diffusion substances move into or out of cells down their concentration gradient through protein channels in the cell membrane. What Does facilitated diffusion require. Channel proteins and carrier proteins are shown but not a gated-channel protein.
Facilitated diffusion is where substances move through the cell membran e with the assistance of transport molecules. Facilitated diffusion is a membrane transport method by which molecules move across the plasma membrane through the concentration gradient with the aid of transmembrane proteins. Facilitated diffusion uses integral membrane proteins to move polar or charged substances across the hydrophobic regions of the membrane.
During facilitated diffusion large ions and polar molecules are dissolved in water and are specifically and passively transported across the cell membrane. Other ions or molecules are also carried across the cell membrane by carrier proteins. Facilitated Diffusion Cells must be able to move large polar and charged molecules across the lipid bilayer of the membrane in order to carry out life processes.
Simple Diffusion moves SMALL and NONPOLAR molecules and Facilitated Diffusion moves LARGE and POLAR molecules. Sodium Na Calcium Ca and Potassium K are all non-polar molecules and will be transported through Simple Diffusion. In some cases molecules pass through channels within the protein.
Polar ions diffuse through transmembrane channels proteins and large molecules diffuse through transmembrane carrier proteins. Facilitated diffusion through the cell membrane. Facilitated diffusion involves the use of a protein to facilitate the movement of molecules across the membrane.
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are similar in that both involve movement down the concentration gradient. Since the transport of molecules occurs through the concentration gradient facilitated diffusion does not use cellular energy for the transport of molecules. Facilitated diffusion is a form of facilitated transport involving the passive movement of molecules along their concentration gradient guided by the presence of another molecule usually an integral membrane protein forming a pore or channel.
A concentration gradient exists for these molecules so they have the potential to diffuse into or out of the cell by moving down it. Facilitated diffusion is important to transport the polar andor large molecules such as sugars and amino acids. Facilitated Diffusion Water moves into tree roots by this process Diffusion.
When transport is accomplished with the expenditure of energy it is referred to as active transport. Certain small nonpolar substances such as. To allow these molecules which are not soluble in the lipid bilayer to pass across the hydrophobic barrier it is necessary to provide ports channels or holes through the membrane.
Water molecules and ions move through channel proteins. In facilitated diffusion molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins such as channels and carriers. Channel proteins can aid in the facilitated diffusion of substances by forming a hydrophilic passage through the plasma membrane through which polar and charged substances can pass.
Facilitated Diffusion This process uses a protein carrier molecules Diffusion. Amino acids and other large molecules are moved through a membrane this way Diffusion. The transport is accomplished passively meaning it isnt driven by the use of ATPenergy in the cell.
It is a selective process which means the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it denying passage to others.

Centrioles And Centrosomes Biology Notes Cell Biology Cell Forms

The Parietal Cells Of The Gastric Glands Secrete Hcl And The Chief Cells Secrete Pepsinogen An Inactive Enzyme Human Digestive System Digestive System Glands

Carbohydrate Digestion Mainly Occurs In The Small Intestine Salivary Amylase Stops Working In The Stomach Due To The Low Biochemistry Digestion Cell Membrane

Cell Membrane Passive And Active Transport Diffusion Osmosis Ac Cell Membrane Cell Transport Cells Project

Are Piles And Hemorrhoids The Same Hemorrhoids Treatment Hemorrhoids Plexus Products

Pin On The Cell And Cellular Transport
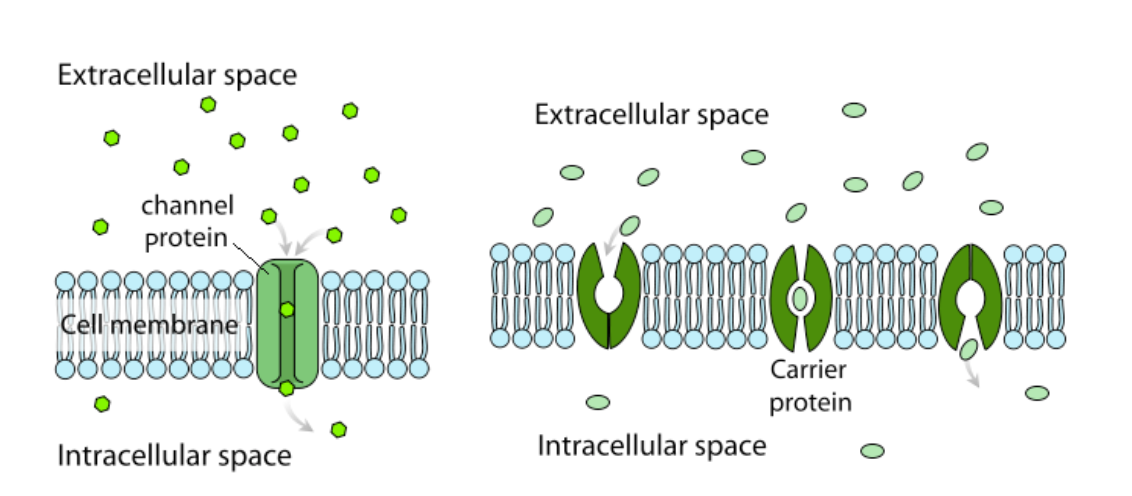
Passive Transport Review Article Khan Academy

Khan Academy Electron Transport Chain Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology

Biology Pictures Cellular Transportation Systems Biology Teaching Biology Biology

Biology Diffusion Osmosis Ch 5 Flashcards Quizlet
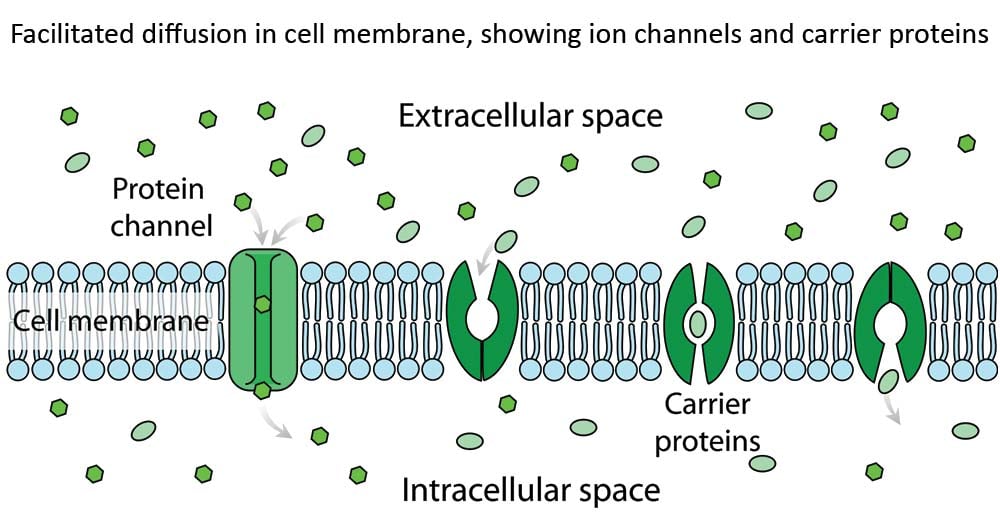
Facilitated Diffusion Definition Principle Factors Examples

Bioknowledgy 1 4 Membrane Transport Membrane Facilitated Diffusion Cell Membrane
Passive Transport Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
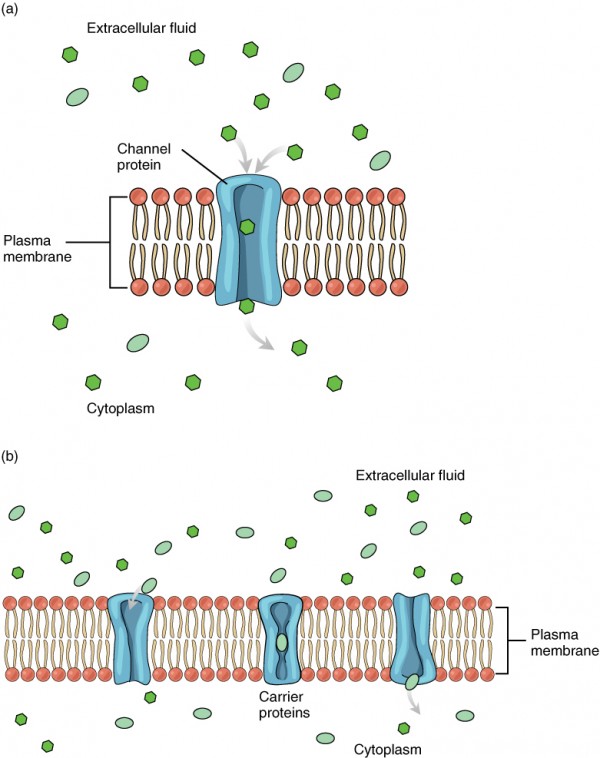
Membrane Transport Anatomy And Physiology

The Plasma Membrane Has A Selective Permeability Quality In Particular This Photo Shows Osmosis Osmosis Is Plasma Membrane Osmotic Pressure Teaching Biology

Sodium Glucose Transport Proteins Sglt Take Up Glucose And Galactose And Transport Them To The Ecf Some Glu Bad Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Digestive System

Class 11th Biology Transport In Plants Biology Transportation Membrane

Posting Komentar untuk "Facilitated Diffusion Moves Large Molecules Through What"