Formation Of Industrial Smog
London is world famous for its episodes of industrial smog. The Formation of Smog Photochemical smog or just smog for short is a term used to describe air pollution that is a result of the interaction of sunlight with certain chemicals in the atmosphere.

Air Pollution Overview Chapter 15 Topics 1 Major Air Pollutants 2 Smog Acid Deposition Ppt Download
Smog was common in industrial areas and remains a familiar sight in cities today.

Formation of industrial smog. Ground-level ozone plays an important role in the formation of smog. 2C O₂ 2CO soot. Industrial Smog Step 2 With Sulfur.
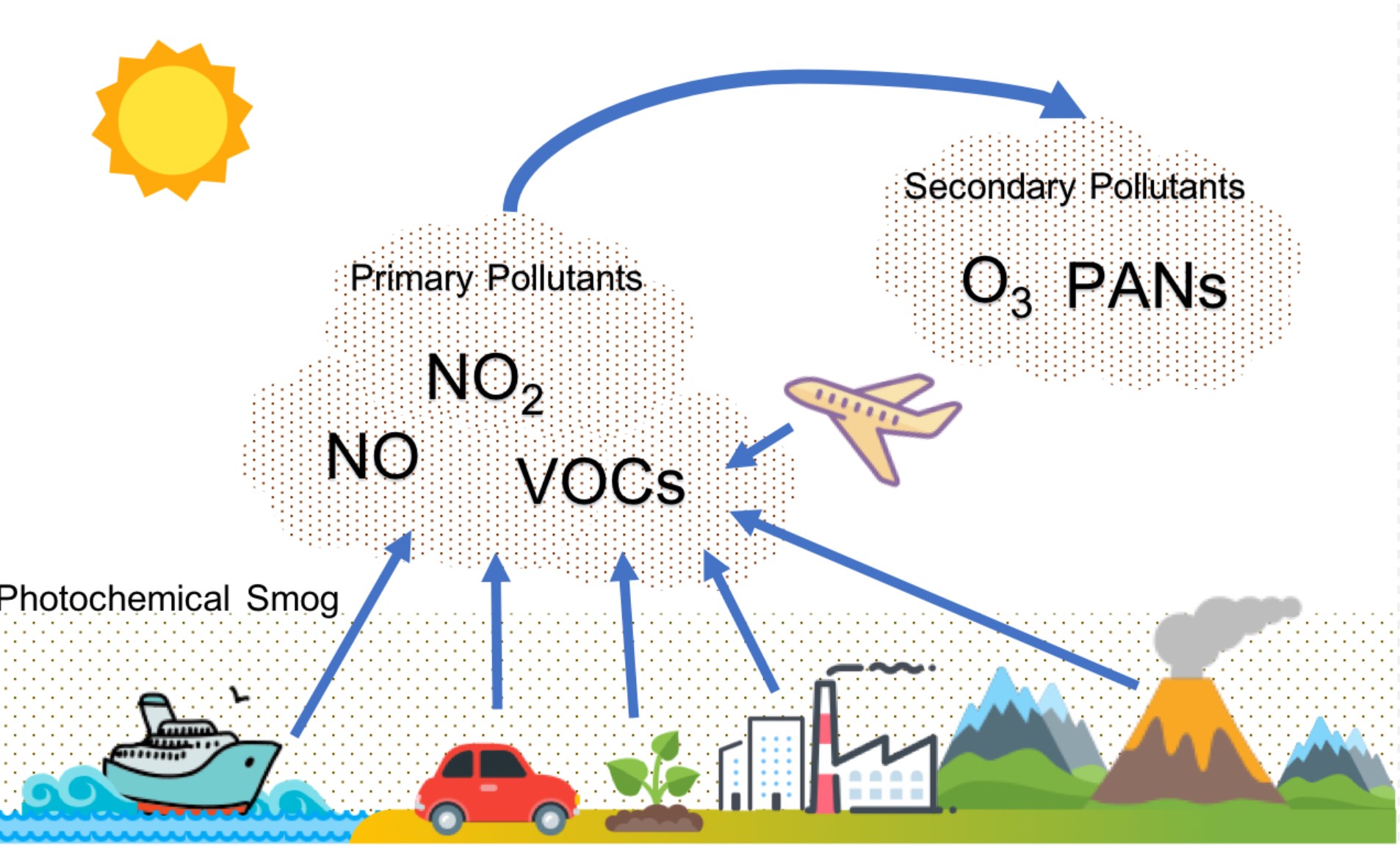
Common examples of secondary pollutants that contribute towards the formation of photochemical smog include aldehydes tropospheric ozone and peroxylacyl nitrates often abbreviated to PAN. It is a layer of warmer that lies on top of colder air preventing the air underneath it from escaping. Under the right conditions the smoke and sulfur dioxide produced from the burning of coal can combine with fog to create industrial smog.
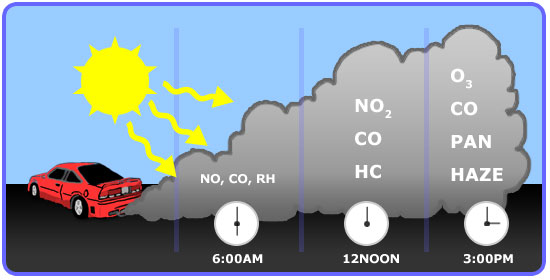
Brief History of Smog Air pollution has been recognized for some time as an urban problem. Photochemical Smog Photochemical smog as commonly seen in the Los Angeles Basin is mainly composed of ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Even in pre-industrial times.
Thus the impacts of smog formation on urban regional and global scales are a cause for concern with regard to overall ecosystem well-being as well as human health. When fossil fuels are burned they release nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere which contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. One of the primary components of photochemical smog is ozone.
Smog the primary constituent of which is ground level ozone is formed by a chemical reaction of carbon monoxide nitrogen oxides VOCs and heat from sunlight. O₂ hydrocarbons NO PANS. Industrial Smog Step 1 with Sulfur S O₂ SO₂.
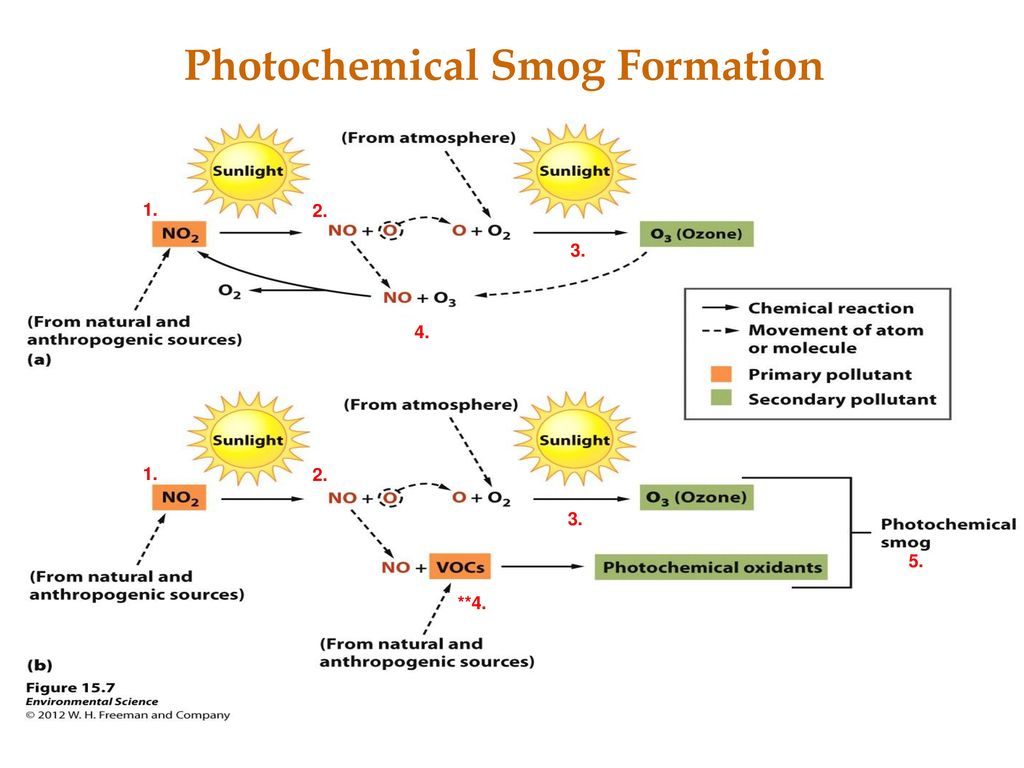
Thus especially cities that are considered to be blessed with good weather are usually suffering most from smog pollution. Photochemical smog is produced when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxide s and at least one volatile organic compound VOC in the atmosphere. Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution due to the reaction of solar radiation with airborne pollutant mixtures of nitrogen oxides NOx and volatile organic compounds hydrocarbons.
Industrial smog typically exists in urban areas where factories burn fossil fuels such as coal which creates smoke and sulfur dioxide that mix with fog droplets to create a thick blanket of haze. Inversion can occur naturally or as a result of the Heat Island Effect. Smog and poor air quality is a pressing environmental problem particularly for large metropolitan cities.
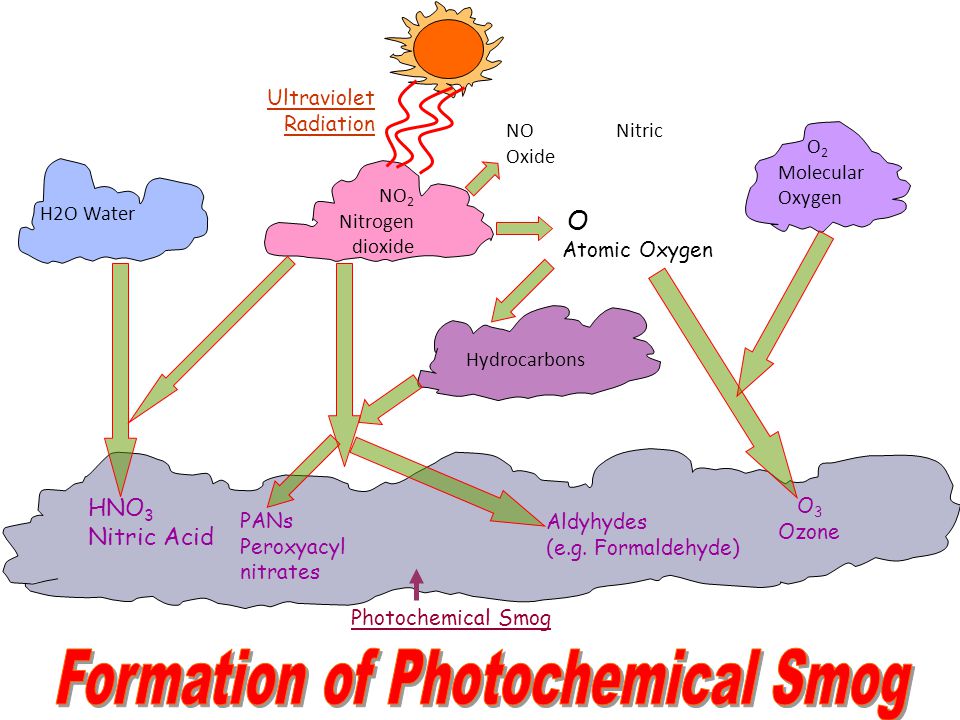
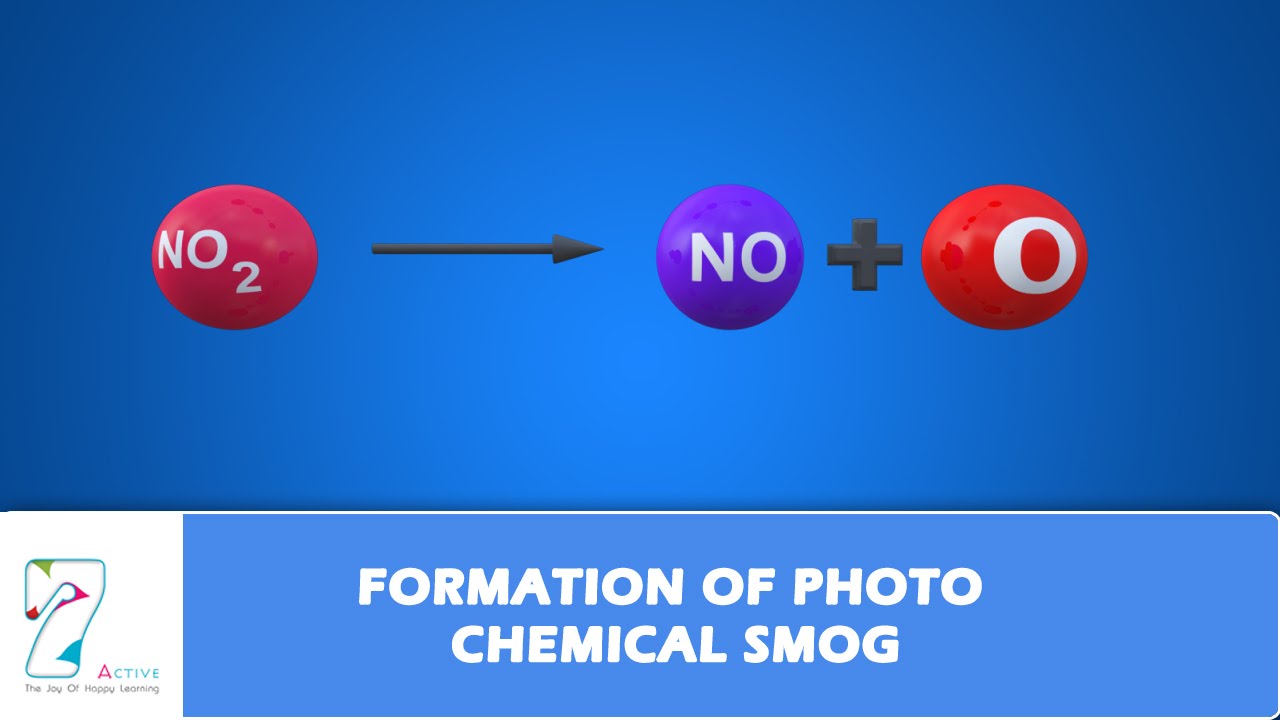
During the formation of ozone nitrogen dioxide from vehicle exhaust is photolyzed by incoming solar radiation to produce nitrogen oxide and. Classic smog forms in areas with high water vapor and high levels of sulfur emissions usually from burning coal. Today most of the smog we see is photochemical smog.
Formation equation for PANS. In high concentrations industrial smog can be extremely toxic to humans and other living organisms. Industrial Smog Primary Pollutant equation 1.
Smog is formed when certain chemicals in our atmosphere interact with the sunlight which in turn leads to visible air pollution which we call smog. Industrial Smog Formation The first element that needs to be in place for smog to form is a temperature inversion layer. Sources of nitrogen from human activities such as electric power generation industry transportation and agriculture can upset the natural balance of nitrogen in the environment.
C O₂ CO₂ soot. Sulfur particles dissolve into water droplets to form sulfuric acid in the atmosphere while coal soot darkens the skies. During peak-traffic hours in the morning large amounts of nitrogen oxides and volatile hydrocarbons are released into the atmosphere.
Formation of smog mechanism The air pollutant primary as well as secondary react with each-other in the presence of sunlight and heat to producing smogg. At ground level Ozone O3 and fine particles are release in air due to complex photochemical reaction between volatile organic compound VOC Sulphur dioxide SO 2 and Nitrogen oxide NO X. Smog is a byproduct of modern industrialization.
Industrial Smog Primary Pollutant equation 2. The process of photochemical smog formation was first identified by Haagen-Smit and Fox 1954 in association with Los Angeles a city whose geography makes it particularly susceptible to this type of smog formation. In 1775 AD English scientist Percival Pott.

Biology 157 Life Science An Environmental Approach Air Pollution Ppt Video Online Download
Ground Level Ozone And Photochemical Smog Egee 102 Energy Conservation And Environmental Protection
What Is Smog Pdf Smog Hydrocarbons
13 5 Photochemical Smog Making Haze While The Sun Shines Chemistry Libretexts
Faculty Of Allied Medical Science Ppt Download
Air Pollution And Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Ppt Download

Chemistry Review Guide 2d Flashcards Quizlet

Chapter 16 Organic Air Pollutant And Photochemical Smog Dr Ahmed Mughari Ppt Download

6 3 Photochemical Smog Ppt Download
Solved What Are The Major Primary Air Pollutants And Their Sources What Are The Secondary Pollutants And How Are They Formed Distinguish Between Course Hero

Atmospheric Science And Air Pollution Chapter Ppt Video Online Download

Chapter 12 1 What Causes Air Pollution Warmup

Apes Pollution Notes Pollution Vocabulary Risk A Measure
Formation Of Photo Chemical Smog Youtube




Posting Komentar untuk "Formation Of Industrial Smog"