Carbon And Hydrogen Bond Type
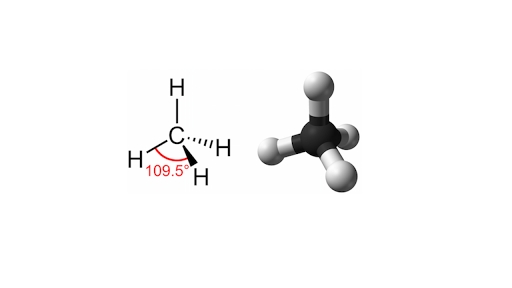
This type of hard bond is known as a sigma bond. The carbon and the four hydrogen atoms form the vertices of a three-dimensional shape known as a tetrahedron which has four triangular faces.
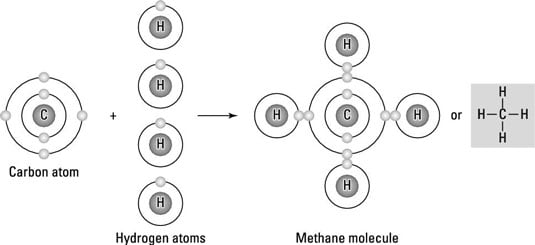
4 Types Of Chemical Bonds Dummies
Bonding between More electronegative element and value Less electronegative element and value Difference in electronegativity Bond Type Sulfur and Hydrogen S 25 H 21 04 C Sulfur and cesium S 25 Cs 07 18 I Chlorine and bromine Cl 30 Br 28 02 C Calcium and chlorine Cl 30 Ca 10 20 I Oxygen and hydrogen.
Carbon and hydrogen bond type. The covalent bond is the most common and strongest form of chemical bonding existing in living organisms. However a molecule may be polar or nonpolar depending on its geometry. In this case the hydrogen atom interacts with electronegative fluorine hydrogen or oxygen.
The carbon-hydrogen bond is nonpolar due to the minimal difference in electronegativities between carbon and hydrogen. A covalent bond is one in which electron pairs are shared. In these molecules each bond is a single bond a single pair of electrons shared between two.
The bonding electrons in polar covalent bonds are not shared equally and a bond moment results. Hydrogen is a chemical element not a type of bond. Because carbon has four valence electrons it can form four covalent.
In the water molecule each hydrogen atom shares one. A carbon atom and a hydrogen atom form a e nonpolar covalent bond. This is commonly seen in carbon-based molecules and also in water an essential molecule found in all living things.
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when ________. For example tetrachloro-methane carbon tetrachloride CCl 4 has polar CCl bonds but the tetrahedral arrangement of the four bonds about the central carbon atom causes the individual bond moments to cancel. A type of chemical bond where two atoms are connected to each other by the sharing of two or more electrons.
One of the atoms sharing electrons is. Carbon is one of the two atoms sharing electrons. Covalent molecules made of only one type of atom like hydrogen gas H2 are nonpolar because the hydrogen atoms share their electrons equally.
Hydrogen molecules are bound together by covalent bonds. Like methane the ammonium ion also has a tetrahedral shape. This link gives you the basics about the hybrid orbitals and you are introduced to the various bonding of carbon in this document.
It can form a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups. The bond between Carbon and Hydrogen is Covalent Bond. FREE Expert Solution.
This type of bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms. Carbon atoms have the ability to bond to themselves and to other atoms with sp sp 2 and sp 3 hybrid orbitals. Methane CH the simplest hydrocarbon molecule consists of a central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
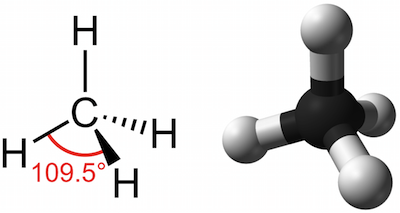
This type of covalent bond is formed whenever there is an equal share of electrons between atoms. In methane for example the central carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms whose positions define the four points of a tetrahedron so that the angle between any two bonds is 1095. Example molecules forming hydrogen bonding as a result of an unbalanced electrostatic potential.
Of a class of organic compounds in which the carbon atoms are arranged in an open chain. All the covalent bonds in methane are identical and the electronic structure of the molecule is described by the molecular orbitals resulting from the overlapping of the valence orbitals in carbon and hydrogen atoms. We are asked to identify the type of bonds joining Carbon and Hydrogen given an illustration.
Identify the type of bond. Inspect the molecule in terms of the type of elements involved and the number of bonds formed. The two atoms sharing electrons are the same elements.
Compounds containing carbon-hydrogen bonds are called organic compounds. Molecules made of more than one type of covalently bonded nonmetal atoms like carbon dioxide gas CO2 remain nonpolar if they are symmetrical or if their atoms have relatively equal pull. Having a closed ring of alternate single and double bonds with delocalized electrons.
In order to minimize repulsive forces the four bonds to hydrogen are arranged tetrahedrally with bond angles of 1095 deg. Because of this methane is said to have a tetrahedral geometry. The bonds are all equivalent and the bonding electrons are more or less pinned between the carbon and hydrogen nucleus.
Hydrogen bonds covalently in most.

Carbon And Carbon Bonding Biology For Non Majors I

Carbon And Hydrocarbons Article Khan Academy
Carbon Bonding Read Chemistry Ck 12 Foundation
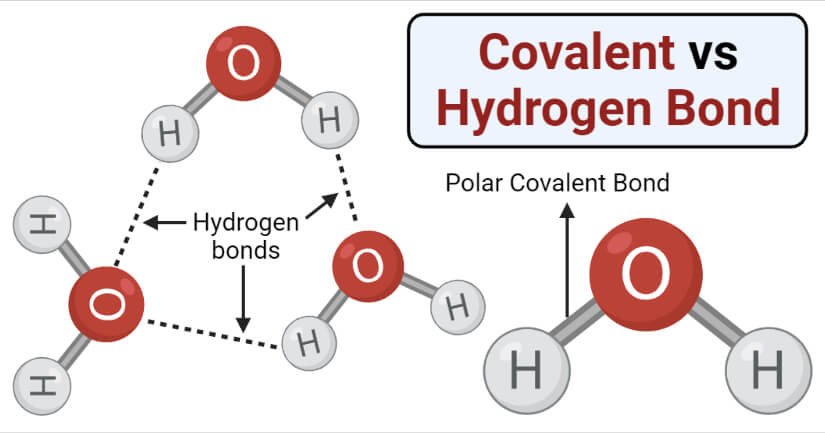
Covalent Vs Hydrogen Bond Definition 11 Key Differences Examples
Carbon Bonding Read Chemistry Ck 12 Foundation
Carbon And Hydrocarbons Article Khan Academy
3 3 Chemical Bonding Biology Libretexts

Chemical Bonds Definition Types And Examples
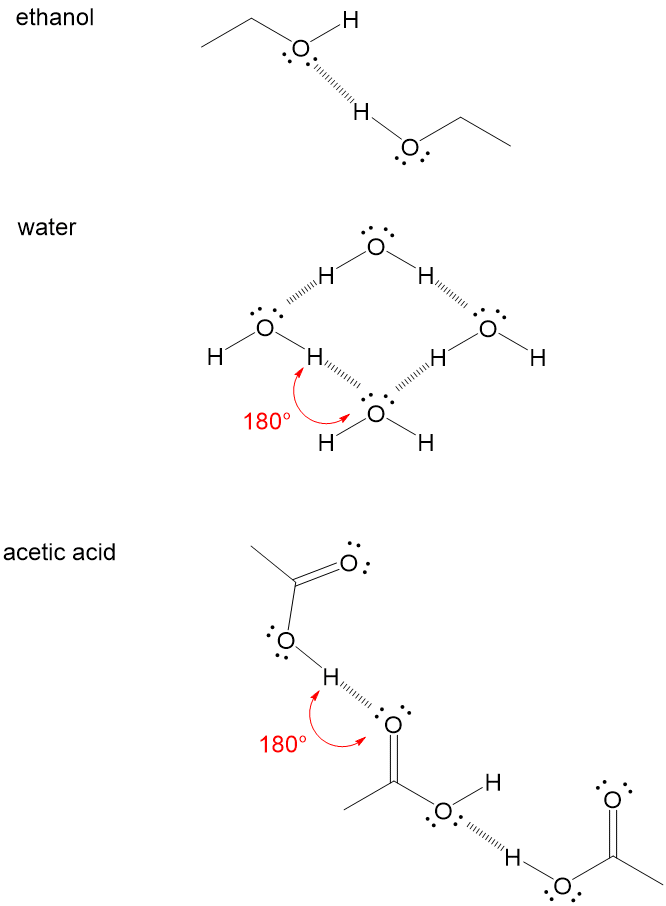
How Do You To Tell When A Hydrogen Bond Will Occur Organic Chemistry Help

Reading Covalent Bonds Biology I

Carbon And Carbon Bonding Biology For Non Majors I

Hydrogen Bonding The Concept Its Characteristics And Importance

Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica

Polar Covalent Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Covalent Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Posting Komentar untuk "Carbon And Hydrogen Bond Type"